Simple Future Tense - Structure, Uses & Examples
Simple Future Tense
Want to talk about tomorrow? Learn Simple Future Tense with my clear explanations and examples.📘 Table of Contents
- 1. Simple Future Verb Structure: Will/Shall + Verb
- 2. When to Use Simple Future Tense?
- 3. Simple Future Tense Sentence Structure: Basic Sentence Patterns
- 4. Simple Future Tense Uses & Examples: Real-Life Sentences
- 5. 100 Simple Sentences & Classroom Examples
- 6. Practice Time!
- 7. FAQs: Simple Future Tense
Let's talk about the simple future tense! This is how we talk about things that will happen later on, like making plans or predictions. Imagine you're thinking about what you'll do tomorrow or next week, like "I will go shopping" or "She will study for her exam."
Here's the easy part: With the simple future tense, you just add "will" or "shall" before the base form of the verb. So instead of saying "I go," you say "I will go."
Why does this matter? Well, lots of people look for help with grammar, English, or learning languages. But sometimes, explanations can be complicated. That's where we come in!
Understanding the simple future tense helps you talk about your plans or what you think will happen. It's like peeking into the crystal ball and seeing what's ahead. Plus, it's super handy for making promises or guessing what might occur.
So if you're learning English or just need a reminder, knowing the simple future tense is awesome. And guess what? It's not as tricky as it might sound!
1. Simple Future Verb Structure: How to Use ‘Will + Base Verb’ Correctly
Verb Structure = will + V (I)
The simple future tense uses will/shall + base verb (V1). Example: I will go, She will cook, They shall arrive.
This is used for future plans or predictions.
- I will play football tomorrow.
- He will pass the exam.
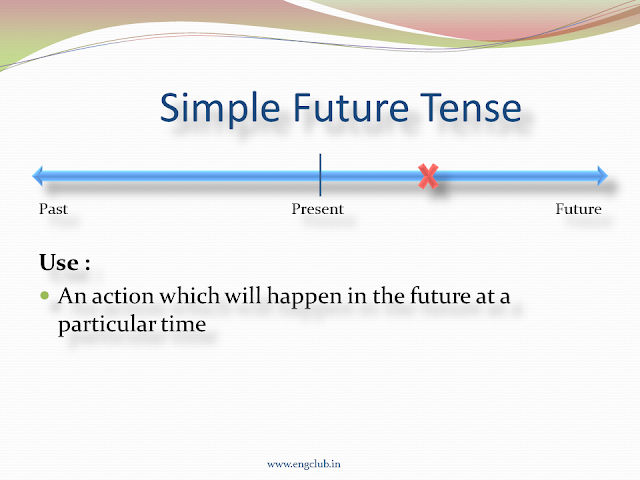
2. When to Use Simple Future Tense? Common Uses and Examples Explained
- We use Simple Future Tense to predict/tell action which will happen in the future at a particular time
- "Going to" and "about to" is used to express that something will happen in the near future which has been already planned.
3. Simple Future Tense Structure: Step-by-Step Grammar Guide for Beginners
3.1 Positive Sentences in Simple Future Tense: Easy Structure and Examples
Positive : S + will + V1 + O.
- I will play football tomorrow.
- You will speak English.
- He will purchase a new car.
- She will make coffee.
- It will rain in next month.
- We will visit Paris in next week.
- They will write a story.
- John will go to school.
- Birds will fly in the sky.
3.2 Negative Sentences in Simple Future Tense: How to Use ‘Will Not’ + Verb
Negative : S + will not + V1 + O.
- I will not play football tomorrow.
- You will not speak English.
- He will not purchase a new car.
- She will not make coffee.
- It will not rain in next month.
- We will not visit Paris in next week.
- They will not write a story.
- John will not go to school.
- Birds will not fly in the sky.
3.3 Yes/No Questions in Simple Future Tense: How to Ask Using ‘Will + Subject + Verb’
Yes/No type questions : Will + S + V1 + O + ?
- Will I play football tomorrow?
- Will you speak English?
- Will you purchase a new car?
- Will she make coffee?
- Will it rain in next month?
- Will we visit Paris in next week?
- Will they write a story?
- Will John go to school?
- Will birds fly in the sky?
3.4 WH Questions in Simple Future Tense: Ask What, Where, When with ‘Will + Subject’
Wh type questions : Wh word + will + S + V1 + O + ?
- Where will I play football tomorrow?
- When will you speak English?
- Which car will you purchase?
- Why will she make coffee?
- Where will it rain in next month?
- When will we visit Paris?
- How will they write story?
- When will John go to school?
- When will birds fly in the sky
4. Simple Future Tense Uses & Examples: Daily Life Sentences to Practice ‘Will + Verb’
1. Future Plans and Intentions:
- I will go to the beach next weekend.
- She will visit her grandparents during the holidays.
2. Predictions Based on Evidence:
- It will rain later today; I can see dark clouds forming.
- He will probably pass the test because he studied hard.
3. Spontaneous Decisions:
- Oh no! I forgot to buy milk. I will go to the store right now.
- We ran out of bread. I will bake some this evening.
4. Promises and Offers:
- I promise I will help you with your homework.
- Don't worry; I will drive you to the airport.
5. Predictions and Assumptions:
- I think she will like the gift; it's exactly what she wanted.
- He won't be late; he's very punctual.
In the simple future tense, actions or events that will happen in the future are described. It's formed by using the auxiliary verb "will" followed by the base form of the main verb.
5. 100 Simple Sentences & Classroom Examples
| Sr. No. | Sentence / Example |
|---|---|
| 1 | I will study English tomorrow. |
| 2 | She will complete her assignment by next week. |
| 3 | We will have a quiz on Friday. |
| 4 | The teacher will explain the lesson in the next class. |
| 5 | They will prepare the project for the presentation. |
| 6 | He will join the class late today. |
| 7 | Will you help me with the homework? |
| 8 | I will not (won’t) forget to bring the books. |
| 9 | She will answer the questions confidently. |
| 10 | We will discuss the topic tomorrow. |
| 11 | The students will submit their reports next Monday. |
| 12 | He will explain the rules before the game. |
| 13 | You will learn many new words this semester. |
| 14 | Will the teacher give us homework today? |
| 15 | She will practice speaking before the test. |
| 16 | We will watch an educational video in class. |
| 17 | The class will start at 9 a.m. tomorrow. |
| 18 | I will participate in the school play next month. |
| 19 | He will read the passage aloud. |
| 20 | They will discuss the answers after the exam. |
| 21 | Will you attend the parent-teacher meeting? |
| 22 | She will bring the study materials. |
| 23 | We will take notes during the lecture. |
| 24 | The teacher will correct our essays tomorrow. |
| 25 | He will explain the homework assignment. |
| 26 | You will improve your English with practice. |
| 27 | They will organize a debate competition next week. |
| 28 | I will review the lesson before the test. |
| 29 | She will ask questions after the lecture. |
| 30 | We will prepare for the science project. |
| 31 | The students will listen carefully during the presentation. |
| 32 | He will write a report on the experiment. |
| 33 | Will you complete your homework on time? |
| 34 | She will join the reading club this year. |
| 35 | We will have a test next Monday. |
| 36 | The teacher will assign group work. |
| 37 | He will explain the new grammar rules. |
| 38 | You will remember the vocabulary words. |
| 39 | They will submit their projects by Friday. |
| 40 | I will study harder for the final exams. |
| 41 | She will present her speech confidently. |
| 42 | We will watch a documentary next week. |
| 43 | The students will answer all questions correctly. |
| 44 | Will the teacher provide extra classes? |
| 45 | He will read the instructions carefully. |
| 46 | You will participate actively in the discussion. |
| 47 | They will organize a quiz competition soon. |
| 48 | I will practice speaking English every day. |
| 49 | She will explain the project guidelines. |
| 50 | We will study for the test this weekend. |
| 51 | The teacher will distribute the worksheets tomorrow. |
| 52 | He will discuss the results with the students. |
| 53 | Will you attend the workshop next week? |
| 54 | She will write an essay on her favorite topic. |
| 55 | We will have a group discussion in class. |
| 56 | The students will read the story silently. |
| 57 | He will explain the answers after the test. |
| 58 | You will learn new things every day. |
| 59 | They will prepare a presentation for the seminar. |
| 60 | I will listen carefully during the lecture. |
| 61 | She will participate in the spelling bee competition. |
| 62 | We will practice the dialogues for the play. |
| 63 | The teacher will check our homework tomorrow. |
| 64 | He will read the poem aloud. |
| 65 | Will you join the extra coaching classes? |
| 66 | She will explain the vocabulary words. |
| 67 | We will review the test results together. |
| 68 | The students will work in pairs during the activity. |
| 69 | He will prepare notes for the exam. |
| 70 | You will improve your speaking skills with practice. |
| 71 | They will submit their assignments before the deadline. |
| 72 | I will study new words every day. |
| 73 | She will attend the English workshop. |
| 74 | We will have a test next week. |
| 75 | The teacher will explain the exam pattern. |
| 76 | He will answer all the questions. |
| 77 | Will you participate in the debate competition? |
| 78 | She will write a story for the contest. |
| 79 | We will discuss the project details tomorrow. |
| 80 | The students will listen to the audio carefully. |
| 81 | He will read the textbook at home. |
| 82 | You will learn faster with regular practice. |
| 83 | They will prepare the charts for the exhibition. |
| 84 | I will review my notes before the exam. |
| 85 | She will join the English speaking club. |
| 86 | We will have a presentation on Friday. |
| 87 | The teacher will explain the homework tomorrow. |
| 88 | He will practice pronunciation daily. |
| 89 | Will you come to the library after class? |
| 90 | She will complete the reading assignment. |
| 91 | We will prepare for the oral test. |
| 92 | The students will answer the questions. |
| 93 | He will write a report on the science project. |
| 94 | You will improve your writing skills. |
| 95 | They will organize a quiz competition soon. |
| 96 | I will listen to English songs to improve. |
| 97 | She will explain the lesson in detail. |
| 98 | We will practice dialogues for the drama. |
| 99 | The teacher will collect the assignments tomorrow. |
| 100 | He will participate actively in the class discussion. |
See also: All 12 English Tenses With 100+ Sentences & Classroom Examples [Easy Guide]
6. Practice Time!
- I _______ (visit) my grandparents next week.
- They _______ (start) the project tomorrow.
- She _______ (not attend) the meeting.
- Will you _______ (join) us for dinner?
- He _______ (finish) his work soon.
- will visit
- will start
- will not (won’t) attend
- join
- will finish
English Tenses Comparison Table
| Tense | Usage | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Present Tense | Daily routines, facts | Subject + base verb / verb+s | She reads every day. |
| Present Continuous Tense | Actions happening now | Subject + is/am/are + verb+ing | I am studying English. |
| Present Perfect Tense | Recently completed actions | Subject + has/have + past participle | They have finished homework. |
| Present Perfect Continuous Tense | From past to now | Subject + has/have been + verb+ing | He has been working since morning. |
| Simple Past Tense | Completed actions in the past | Subject + past verb | We visited the zoo yesterday. |
| Past Continuous Tense | Specific time past actions | Subject + was/were + verb+ing | She was cooking at 8 PM. |
| Past Perfect Tense | Before another past action | Subject + had + past participle | They had left before I arrived. |
| Past Perfect Continuous Tense | Ongoing past action | Subject + had been + verb+ing | I had been reading for two hours. |
| Simple Future Tense | Future facts or decisions | Subject + will + base verb | She will call you tomorrow. |
| Future Continuous Tense | Action in progress in future | Subject + will be + verb+ing | I will be sleeping at 11 PM. |
| Future Perfect Tense | Done before a future time | Subject + will have + past participle | We will have arrived by noon. |
| Future Perfect Continuous Tense | Ongoing till future time | Subject + will have been + verb+ing | She will have been working for 5 years. |
📘 Learn All 12 English Tenses
7. FAQs: Simple Future Tense
1. What is the Simple Future Tense?
2. When do we use it?
3. How do we form it?
4. Common mistakes?
5. Questions and negatives?
References
- Murphy R. (2019). English grammar in use: A self-study reference and practice book for intermediate learners of English (5th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
- Purdue University Online Writing Lab. (n.d.). Verb tense consistency. https://owl.purdue.edu
- BBC Learning English. (n.d.). Grammar lessons: Simple future tense. https://www.bbc.co.uk/learningenglish
- Dave’s ESL Cafe. (n.d.). Grammar lessons for English learners. https://www.eslcafe.com
- Quirk R., Greenbaum S., Leech G. & Svartvik J. (1985). A comprehensive grammar of the English language. Longman.
- Azar B. S. (2009). Understanding and using English grammar (4th ed.). Pearson Education.
- Swan M. (2005). Practical English usage (3rd ed.). Oxford University Press.
- Eastwood J. (1994). Oxford guide to English grammar. Oxford University Press.
- Thomson A. & Martinet A. V. (1986). A practical English grammar (4th ed.). Oxford University Press.
- Celce-Murcia M., & Larsen-Freeman D. (1999). The grammar book: An ESL/EFL teacher's course (2nd ed.). Heinle & Heinle Publishers.
- Seely J. (2004). Oxford English grammar course: Basic. Oxford University Press.
- Nunan D. (2003). Practical English language teaching (2nd ed.). McGraw-Hill.
- Richards J. C., & Schmidt R. (2010). Longman dictionary of language teaching and applied linguistics (4th ed.). Pearson Education.
- Lewis M. (1993). The English verb: An exploration of structure and meaning (2nd ed.). Collins ELT.
- Hewings M. (2005). Advanced grammar in use (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press.
- Biber D., Conrad S., & Leech G. (2002). Longman grammar of spoken and written English. Pearson Education.
- Carter R., & McCarthy M. (2006). Cambridge grammar of English: A comprehensive guide to spoken and written grammar and usage. Cambridge University Press.